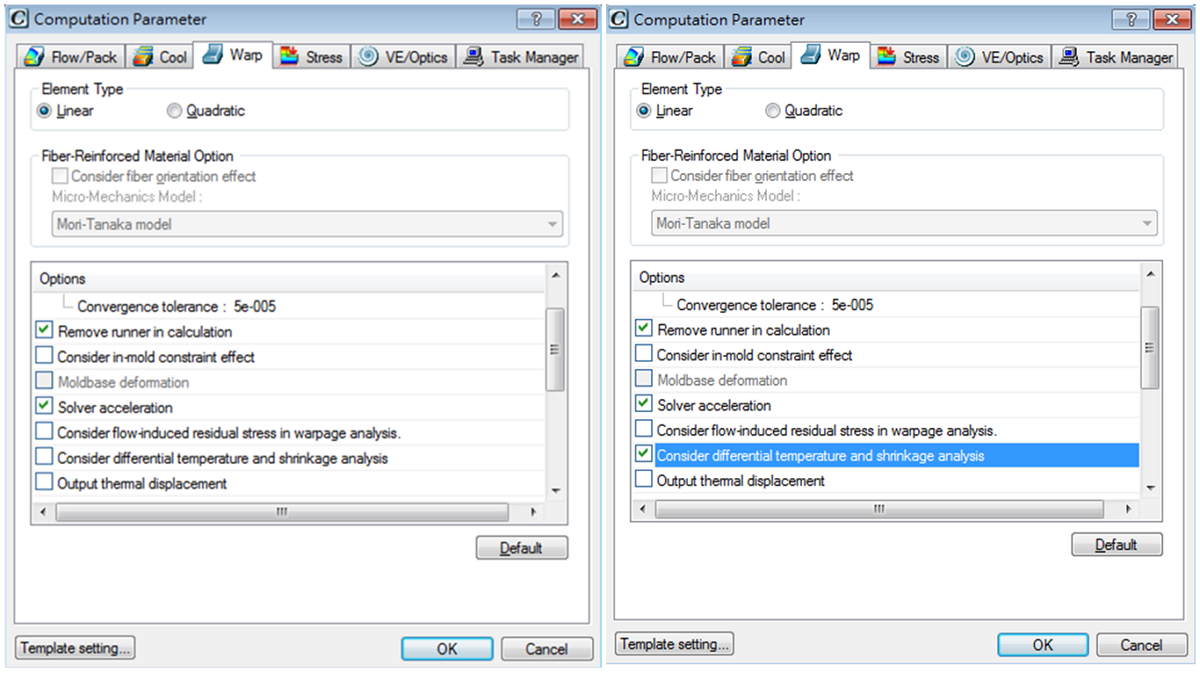
Differential temperature (P.S.1) and differential shrinkage effects (P.S.2) are the two main factors that cause product displacement. Thus, if we are able to check how these two factors affect warpage, we will have a better understanding of how we can better improve warpage issue. The latest release of Moldex3D R13 allows users to check these two effects separately in displacement analysis results.
Step 1. Open the Computation Parameter window before starting an analysis process. Check Consider differential temperature and shrinkage analysis under Warp tab.
Step 2. After the analysis, the effects of Differential temperature effect displacement and Differential shrinkage displacement will be available in the warpage analysis results.
 |
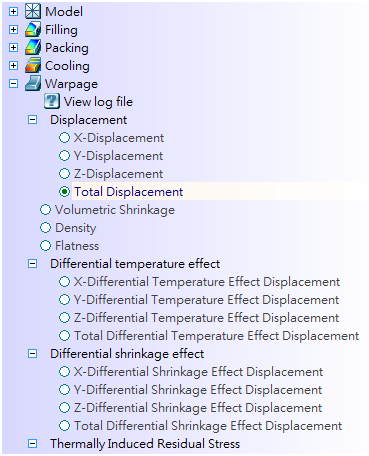 |
The list of warpage analysis results when Consider differential temperature and shrinkage analysis is checked |
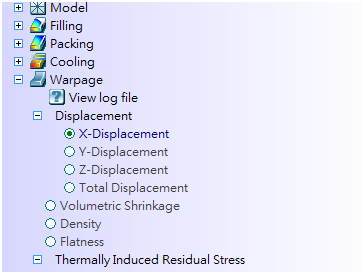
The list of warpage analysis results when Consider differential temperature and shrinkage analysis is not checked |
Step 3. In the following case, the differential shrinkage effect is a greater influential factor affecting the displacement result than the differential temperature effect. That is, the differential shrinkage effect is the major concern if we would like to reduce warpage.
 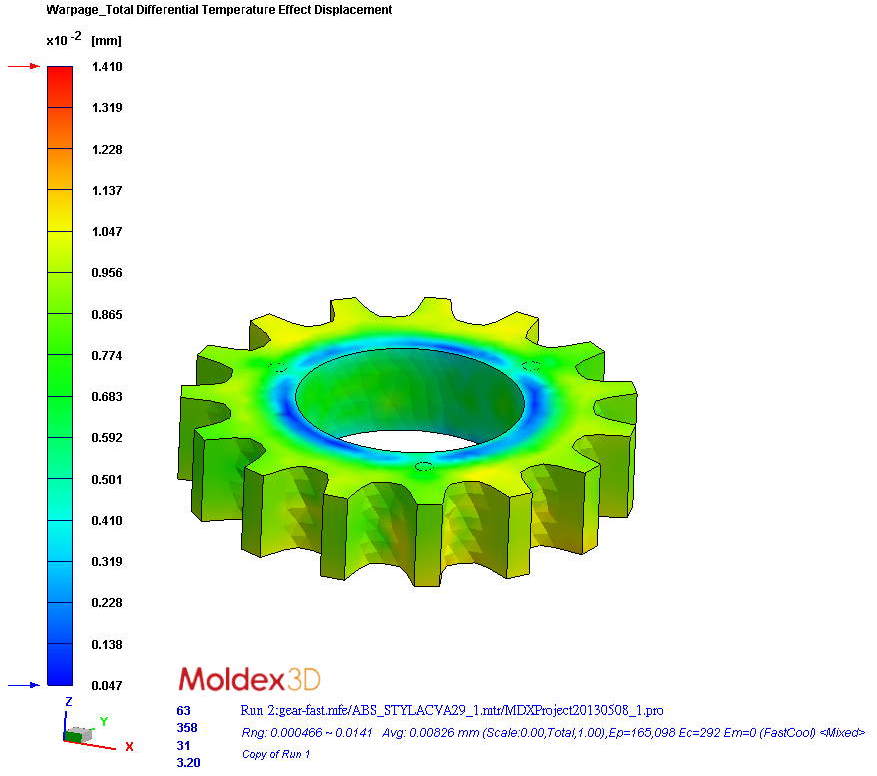 |
  |
Differential temperature effect displacement |
Differential shrinkage effect displacement |
P.S. 1. Differential temperature effect displacement is calculated with the difference of volumetric shrinkage through thickness. The differential temperature effect displacement represents the out-of-plane warpage.
P.S. 2. Differential shrinkage displacement is calculated with the distribution of thickness average volumetric shrinkage on the same cutting plane. The differential shrinkage displacement represents the in-plane shrinkage due to PVT distribution.
Plastic Mould Steel,Plastic Mold Steel
Jiangyou ChongxinSpecial Metal Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.zhongxindiesteel.com
