Carbon steel seamless pipes are known for their strength and durability, thanks to their seamless structure that eliminates potential weak points. They maintain a consistent mechanical performance throughout their length due to their standard shape and design. Additionally, they offer better resistance at high temperatures because of the absence of joints.
These pipes provide higher accuracy in terms of size and thickness, ensuring more predictable performance across various environments.
On the other hand, carbon steel welded pipes may have lower strength and durability compared to seamless ones. This is mainly due to the welding process itself, which can cause changes in microstructure and mechanical properties in the heat-affected zone, potentially leading to reduced toughness and resistance to wear.
Welded pipes might also have visible weld beads and heat-affected areas on their surface, which could require additional treatment or cleaning to meet specific requirements.
Seamless carbon steel pipes are commonly used in:
High-pressure applications: These are often preferred in the oil and gas industry for transporting liquids under high pressure, as there's no risk of leakage.
Hydraulic systems: They are suitable for such applications due to their ability to withstand high pressure and smooth interior surfaces that reduce friction loss.
Critical liquid transport: Used in essential applications where pipe strength is crucial, such as in chemical processing, nuclear plants, and power generation industries.
Welded carbon steel pipes are typically used in:
Medium pressure and temperature: Suitable for applications requiring medium pressure and temperature, like low-pressure steam systems.
Non-corrosive fluids: Ideal for moving non-corrosive fluids where there's minimal risk of corrosion, such as water distribution systems.
Manufacturing Process
Seamless carbon steel pipes are manufactured by extruding a solid steel bar to create a hollow pipe, resulting in no joints or welds, thus ensuring a uniform design.
Welded carbon steel pipes are produced by rolling a flat plate into a cylindrical shape and then welding it. Common welding methods include longitudinal (LSAW) and spiral (SSAW) welding.
Why Choose?
Seamless carbon pipes offer superior strength and reliability, especially in critical applications where high pressure conditions are involved.
Welded carbon pipes are cost-effective, easier to manufacture, and ideal for medium pressure and temperature applications.
Table of contents
- Carbon Steel seamless and welded pipe manufacturing process
- Seamless vs Welded Carbon Steel Pipe Specification
- Carbon steel Welded and seamless pipe equivalent
- Tolerances for hot finished seamless pipe
- Tolerances for cold drawn welded tubes
- Carbon Steel seamless and welded pipes chemical composition
- CS Welded and Seam Pipe mechanical properties
- List of documents to import Low Temp Welded Pipe
- A106 Seamless and Welded Pipe Schedule
- CS Welded and Seamless Pipe International Standard
- Hot finished welded type tubes sizes in mm
- Difference between seamless pipe and erw pipe
- Maximum Allowed Stress of DIN EN 10220 seamless steel pipes
- Low Temp Seamless Pipe Charpy V-Notch Impact Tests
- Hot Forming and Heat Treatment of CS ERW and Seamless pipe
- List of machinery to produce seamless pipe
- List of machinery to produce welded pipe
- Testing for Seam pipe and ERW Pipe
List of Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe grades for high-temperature service, check uses and manufacturing process of CS SMLS and Welded pipes
Carbon Steel seamless and welded pipe manufacturing process
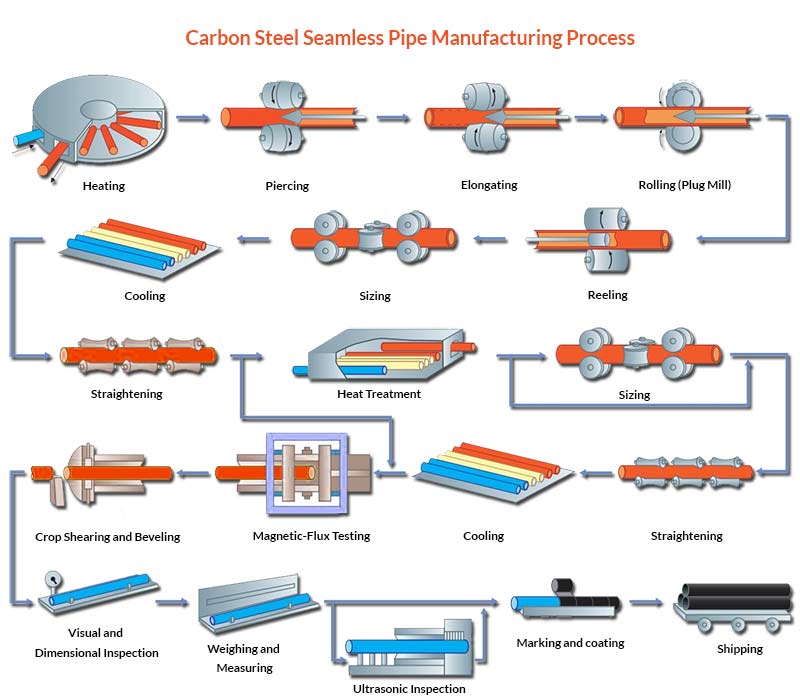
Carbon steel seamless pipe manufacturing process

Carbon steel welded pipe manufacturing process
Check Carbon Steel welded and seamless pipe specifications, equivalent, tolerances, and properties
Seamless vs Welded Carbon Steel Pipe Specification
| Size Range | Wall thickness | OD |
|---|---|---|
|
|
1/2†to 60†|
| High carbon steel seamless pipe sizes | Indian standards | Size |
|
|
|
| AMS standard | Hardness range | Maximum operating temperature |
|
767 HB |  650°C (1202°F). |
| Expansion coefficient | Joining methods | Yield strength |
| 12×10-6/°C |
|
35,000 psi. |
| Plain carbon steel pipes form | Estimated delivery time | SWG |
|
|
|
| Services | Meet the requirements | Length |
|
|
|
| Density | Temperature range | Melting point |
| 7.85 g/cm3 to 8.05 g/cm3. | 2200°F | 1425-1540°C (2597-2800°F) |
| BS standards | Black steel CS pipe classification | Manufacturing technique |
|
|
|
| Marking | Applications | Welding procedure |
|
|
|
| Weight calculator formula | Features | Certification |
|
|
|
| Origin of material | Standards | Coatings |
|
|
|
| Packaging | Carbon steel pipe equipment | Testing requirements |
|
|
|
Carbon steel Welded and seamless pipe equivalent
| DIN | BS | NFA | ASTM |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIN 17175 Grade 17 Mn 4 | NFAA 49-213 Grade TU 48-c | ASTM A106 Grade C | ASME SA 106 Grade C |
Tolerances for hot finished seamless pipe
| Outside Diameter Range (inches) |
Wall Percent of O.D. |
Unannealed or Stress Relief Annealed |
Oil Quenched & Tempered |
Soft Annealed or Normalized |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O.D. Inches | I.D. Inches | O.D. & I.D. | O.D. Inches | I.D. Inches | ||||||
| Plus | Minus | Plus | Minus | Plus/Minus | Plus | Minus | Plus | Minus | ||
| Up to 0.499 | All | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.002 | ||||
| 0.500-1.699 | All | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.007 |
| 1.700-2.099 | All | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| 2.100-2.499 | 0.007 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.008 | |
| 2.500-2.899 | All | 0.008 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.009 |
| 2.900-3.299 | All | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.011 |
| 3.300-3.699 | All | 0.010 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.013 |
| 3.700-4.099 | All | 0.011 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.011 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| 4.100-4.499 | All | 0.012 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.012 | 0.015 | 0.014 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.011 |
| 4.500-4.899 | All | 0.013 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.013 | 0.017 | 0.016 | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.012 |
| 4.900-5.299 | All | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.013 |
| 5.300-5.549 | All | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.020 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.014 |
| 5.550-5.999 | Under 6 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.025 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.018 |
| 6 to 7 1/2 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.023 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.016 | |
| Over 7 1/2 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.016 | |
Tolerances for cold drawn welded tubes
| Size Range Inch (mm) |
OD Tolerance Inch (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Over | Under | |
| Up to 2.999 (76.17) | 0.020 (0.51) | 0.020 (0.51) |
| 3.000-4.499 (76.20-114.27) | 0.025 (0.64) | 0.025 (0.64) |
| 4.500-5.999 (114.30-152.37) | 0.031 (0.79) | 0.031 (0.79) |
| 6.000-7.499 (152.40-190.47) | 0.037 (0.94) | 0.037 (0.94) |
| 7.500-8.999 (190.50-228.57) | 0.045 (1.14) | 0.045 (1.14) |
| 9.000-10.750 (228.60-273.05) | 0.050 (1.27) | 0.050 (1.27) |
| 10.750 and larger | 1% | 1% |
Carbon Steel seamless and welded pipes chemical composition
ASTM A53
| Values in % | Type S (Seamless) |
Type F (Furnace Weld) |
Type E (ERW) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A53 | Grade A | Grade B | Grade A | Grade A | Grade B |
| Manganese | 0.95 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.95 | 1.2 |
| Carbon | 0.25 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 0.3 |
| Sulfur | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Phosphorous | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Nickel | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Copper | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Molybdenum | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Chromium | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Vanadium | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
ASTM A106
| Element | Mn | C max |
S max |
P max |
Cr max (3) |
Si min |
Mo max (3) |
Cu max (3) |
V max (3) |
Ni max (3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade A | 0.27-0.93 | 0.25 (1) | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.40 |
| Grade B | 0.29-1.06 | 0.30 (2) | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.40 |
| Grade C | 0.29-1.06 | 0.35 (2) | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 0.40 |
ASTM A333
| Element | Grade 3 | Grade 6 |
|---|---|---|
| C | 0.19 | 0.30 |
| Mn | 0.31–0.64 | 0.29–1.06 |
| P | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| S | 0.025 | 0.025 |
| Si | 0.18–0.37 | 0.10 min |
| Ni | 3.18–3.82 | 0.40 |
| Cr | … | 0.30 |
| Cu | … | 0.40 |
| Al | … | … |
| V | … | 0.08 |
| Cb | … | 0.02 |
| Mo | … | 0.12 |
| Co | … | … |
CS Welded and Seam Pipe mechanical properties
ASTM A53
| Seamless and ERW | A53 Grade B | A53 Grade A |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | 35,000 | 30,000 |
| Tensile Strength, min, psi | 60,000 | 48,000 |
ASTM A106
| ASTM A106 | Grade A | Grade B | Grade C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength, min., psi | 30,000 | 35,000 | 40,000 |
| Tensile Strength, min., psi | 48,000 | 60,000 | 70,000 |
ASTM A333
| ASTM A333 | Yield Strength, min. | Tensile Strength, min. | Elongation %, min. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | psi | MPa | psi | MPa | Longitudinal | Transverse |
| Grade 3 | 35 000 | 2 Guangzhou Casselin Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.casselinautoparts.com | ||||
